Fungai’s Fight Against Climate Change: Nature’s Solution for Climate Change and Carbon Removal”
The researchers confirmed this on Monday. That underground fungus can absorb approximately one-third of the Earth-warming carbon emissions that occurs from burning oil, coal, and gas. Before, this amount was unknown; however, it has the potential to be further expanded. Mycorrhizal fungi hold up to 13 gigatons, or 36%, of annual global fossil fuel CL00, -0.56% emissions below ground. To gain an understanding of the importance of this percentage. This is more than the carbon China emits each year. The globe’s top polluters can be identified as China, the US, and India. As such, fungi “represent a blind spot in carbon modeling, conservation, and restoration,” study coauthor Katie Field, a professor of biology at the U.K.’s University of Sheffield, said in a release. “The numbers we’ve uncovered are jaw-dropping,” Field said. Unveiling Fungi’s Role: The fungi create a major underground system all over the planet underneath the forests and grasslands,…
The researchers confirmed this on Monday. That underground fungus can absorb approximately one-third of the Earth-warming carbon emissions that occurs from burning oil, coal, and gas. Before, this amount was unknown; however, it has the potential to be further expanded.
Mycorrhizal fungi hold up to 13 gigatons, or 36%, of annual global fossil fuel CL00, -0.56% emissions below ground. To gain an understanding of the importance of this percentage. This is more than the carbon China emits each year. The globe’s top polluters can be identified as China, the US, and India.
As such, fungi “represent a blind spot in carbon modeling, conservation, and restoration,” study coauthor Katie Field, a professor of biology at the U.K.’s University of Sheffield, said in a release.
“The numbers we’ve uncovered are jaw-dropping,” Field said.
Unveiling Fungi’s Role:
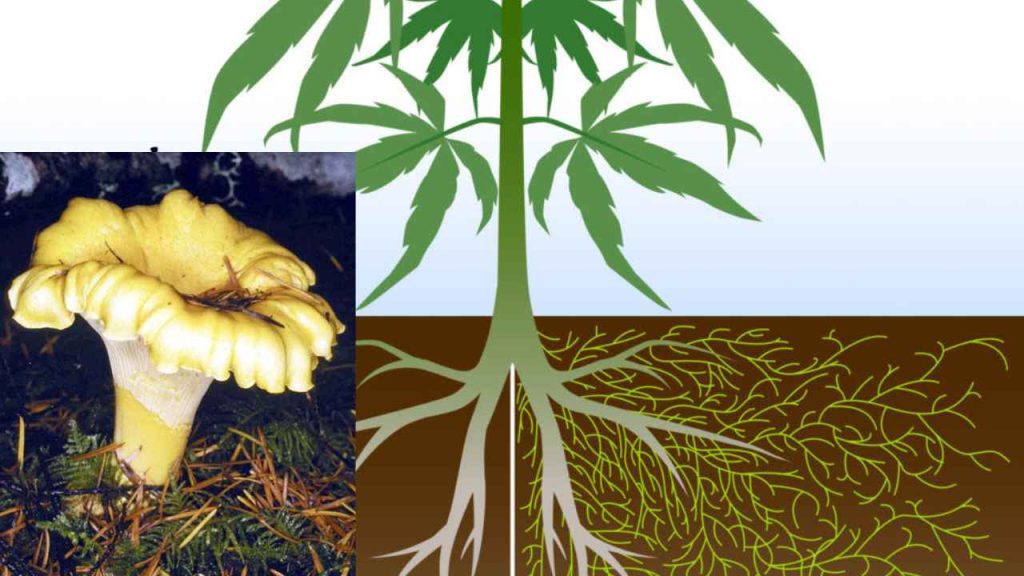
The fungi create a major underground system all over the planet underneath the forests and grasslands, as well as houses, gardens, and roads on every continent on Earth.
Scientists have discovered that mycorrhizal fungi have a mutually beneficial relationship with land plants, and can accumulate carbon. These fungi associate with plants, aiding them in transferring carbon in the form of fats and sugars into the soil. However, the right amount of carbon accumulated by these fungi has remained unsure.
Harnessing Nature’s Solution:
The research by a team of scientists, with researchers from the University of Sheffield discovered. That fungi preserving over a third of the carbon evolved from fossil fuel emissions each year depicts that it could be important as countries strive to address climate change and achieve carbon neutrality.
The research disclosed in Current Biology, disclosed that approximately 13.12 gigatons of CO2 are transmitted from plants to fungi yearly. This will convert the soil beneath our feet into an enormous carbon pool and the most useful carbon capture storage unit in the world.
Greenhouse gases and carbon dioxide act like a cap or a blanket, capturing a portion of the warmth that Earth could have otherwise emitted into space. Worldwide release of CO2 from burning fossil fuels totals about 34 billion metric tons per year. About 45% of this is from coal, about 35% from oil, and about 20% from gas NG00, -0.13%.
Benefits and Implications:
As the world gradually shifts away from fossil fuels. The most affluent seven nations highlighted the vitality of enhancing efforts to achieve the existing climate goals. These goals consist of reducing carbon emissions by roughly 43% by 2030 and 60% by 2035. In comparison to the levels recorded in 2019, there has been a significant change.
Because of their significant role in reducing carbon emissions. Researchers are urging policymakers to consider fungi in conservative policies and biodiversity efforts. At the existing rate, the United Nations alerts that 90% of soils could be damaged by 2050. Scientists caution that this could pose dangers not only for controlling climate change and rising temperatures but also for crop productivity and harvest.
Professor Toby Kiers, senior author from Vrije University Amsterdam added. “The paper is part of a global push to understand the role that fungi play in Earth’s ecosystems. We know that mycorrhizal fungi are vitally important ecosystem engineers, but they are invisible to most people.”
Biodiversity is important to maintain the health of oceans. And can help to meet the food demands of the rising global population. We can identify that Fungi play a major role in reducing drastic climate change.





