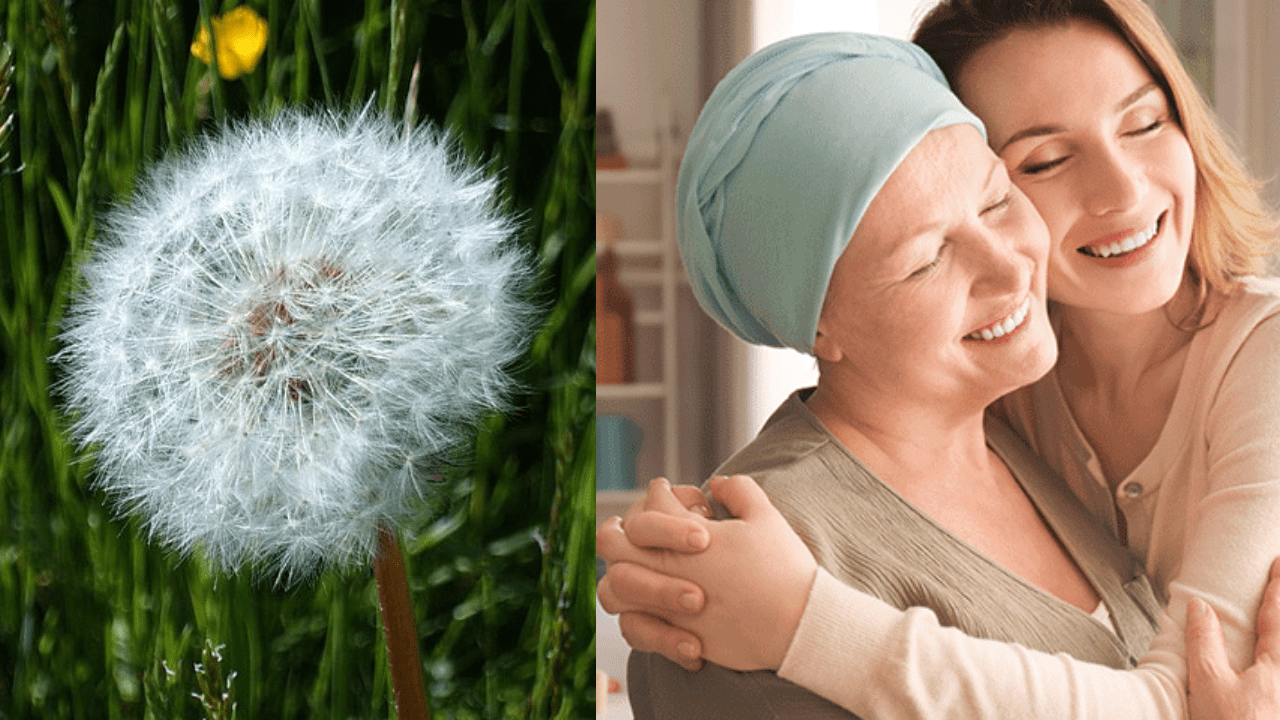
Breast cancer is a major health challenge that affects millions worldwide. In a recent breakthrough study published in Scientific Reports, researchers have uncovered some groundbreaking findings in the battle against breast cancer. The extract from a ‘dandelion flower‘ seems to be a game-changer in fighting cancer, according to the study.
Breast cancer is influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and the environment. However, there is no one particular cause for cancer cells to grow or emerge. Treating is tough because it can spread to other parts of the body. Existing treatments can work, but they often bring harsh side effects like nerve problems, kidney issues, and heart troubles. The effects can severely impact a patient’s quality of life. Therefore, the scientists focused on a Natural health product that can be used as a therapeutic agent.
Going Natural
Lately, researchers have been looking into natural products, like plants, as possible solutions. These natural products seemingly have fewer side effects and potent therapeutic effects. One of these natural options is dandelion extract.
Dandelion’s Hidden Power
Dandelion, a member of the Asteraceae family, is often known as a weed than a potent medicinal plant. However, recent scientific investigations have found its remarkable potential. Dandelion organs contain flavonoids and L-chicoric acid. These compounds exhibit anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
So, what did the scientists find in their study? They wanted to see how dandelion extract, along with something called all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), would affect two types of breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7.
Following are some of the remarkable things they noticed:
Stopping Growth: The dandelion extract slowed the growth of cancer cells. This is a good sign because slower growth can mean it’s easier to control cancer.
Less Inflammation: The treatment also made the cells less inflamed. Inflammation can help cancer grow, so reducing it is a good thing.
Genes at Work: The researchers looked at the genes inside the cells and found some changes. They noticed that dandelion extract increased the activity of some genes that can fight cancer.
Metastasis Control: One important discovery was that dandelion extract seemed to slow down the spread of cancer cells. This is crucial because stopping cancer from spreading is a big challenge in treating breast cancer.
What Does It All Mean?
The study suggests that dandelion extract might help treat breast cancer. It seems to slow down the growth of cancer cells, reduce inflammation, and even hinder the cells from spreading to other parts of the body!
However, more research is needed to understand exactly how dandelion extract works. Along with understanding if it’s safe and effective for people with breast cancer.
The discovery of dandelion extract’s potential as a breast cancer fighter is exciting. As scientists continue their work, they might uncover more about dandelion extract and its role in treating cancer. Every step forward is a step closer to finding better and kinder ways to beat this tough disease.
Conclusion
In a recent breakthrough study published in Scientific Reports, researchers have uncovered some groundbreaking findings in the battle against breast cancer. The extract from a ‘dandelion flower’ seems to be a game-changer in fighting cancer, according to the study. It seems to slow down the growth of cancer cells, reduce inflammation, and even hinder the cells from spreading to other parts of the body! However, more research is needed to understand exactly how dandelion extract works.
Journal Reference;
Rezaie H, Alipanah-Moghadam R, Jeddi F, et al. (2023). Combined dandelion extract and all-trans retinoic acid induces cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells. Sci Rep.
doi:10.1038/s41598-023-42177-z. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-42177-z
Also read,